Oxygen consumption, commonly known as VO2 Max, is one of the most important factors in determining the performance of an athlete, and more specifically of a runner or trail runner as in our case. This parameter measures the maximum amount of oxygen that a person can use during intense exercise and is a fundamental indicator of a person's aerobic capacity. At RUNNEA we are going to try to explain the relationship between oxygen consumption and running performance, taking into account the known scientific evidence.

What is VO2 max?
VO2 max is expressed in milliliters of oxygen per kilogram of body weight per minute (ml/kg/min). This value reflects the body's ability to carry and use oxygen during exercise. The higher the VO2 max, the greater the athlete's ability to sustain prolonged exertion. It is crucial to understanding the upper limit of aerobic performance.
Not sure which shoe to choose?
In a few simple steps we help you to choose the ideal running shoe for you.
GO TO THE RECOMMENDERThe physiology behind VO2 max
To better understand the concept of VO2 max, it is necessary to break down its physiology. The transport and use of oxygen in the body involves several systems:
- Respiratory system: the lungs are responsible for the absorption of oxygen from the air.
- Cardiovascular system: The heart and blood vessels transport oxygen from the lungs to the active muscles.
- Muscular system: Muscles use oxygen to produce energy through the process of oxidative phosphorylation.
VO2 max is influenced by the efficiency of each of these systems. A runner with a high VO2 max has a highly efficient cardiovascular and pulmonary system, as well as muscles adapted for high oxygen consumption.

Factors affecting VO2 max
- Genetics: Genetics plays a crucial role in VO2 max. Research has shown that genetic variability can explain up to 50% of the differences in VO2 max between individuals.
- Training: Regular training, especially aerobic training, can increase VO2 max. Well-structured programs can increase this value by 10% to 20% in untrained individuals.
- Age: VO2 max tends to decrease with age. However, constant training can mitigate this reduction.
- Sex: On average, men have a higher VO2 max than women due to differences in body composition and blood volume.
- Altitude: Training at altitude can improve VO2 max as the body adapts to the lower availability of oxygen, improving the efficiency of its use.

Measuring VO2 max
VO2 max can be measured in a laboratory using stress tests with specialized equipment. These tests usually involve running on a treadmill or pedaling a stationary bike while measuring oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production. Common tests include:
- Progressive stress test: involves gradually increasing the intensity of exercise until exhaustion while measuring gas exchange.
- Cooper's test: A field method that estimates VO2 max based on distance traveled in 12 minutes.
- Leger test (or course navette): Consists of running between two points 20 meters apart to the rhythm of sound signals that are progressively accelerated.
Importance of VO2 max in runners
If we manage to have a high VO2 max it will allow us as runners to:
- Maintain higher speeds: Runners with a high VO2 max can sustain faster paces for longer, which is essential in long distance races.
- Recover better: Improved ability to recover between intense training sessions, allowing for more frequent and higher volume training.
- Improve energy efficiency: Higher oxygen consumption translates into better utilization of the body's energy sources, such as carbohydrates and fats.

Strategies to improve VO2 max
High-intensity interval training (HIIT): This type of training has been shown to be very effective in increasing VO2 max. It consists of alternating periods of maximal effort with periods of active recovery.
Example of a HIIT session:
- Warm-up: 10 minutes of gentle jogging.
- Intervals: 4 minutes at near maximum pace, followed by 4 minutes of active recovery (light jogging or brisk walking). Repeat 4 times.
- Cool down: 10 minutes of light jogging.
Continuous low intensity training: Prolonged sessions at a moderate pace are also essential to improve aerobic capacity. This type of training increases blood volume and oxygen transport efficiency.
Example of low intensity session:
- Continuous 60-90 minute run at 60%-70% of maximum heart rate.
Strength training: supplementing running with strength exercises improves muscle efficiency and contributes to a higher VO2 max. Strength training helps improve running economy and muscular endurance.

Example of a strength session:
- Squats: 3 sets of 12 reps.
- Deadlifts: 3 sets of 10 reps.
- Lunges: 3 sets of 12 repetitions per leg.
- core exercises (plank, crunches): 3 sets of 30 seconds each.
Proper nutrition: A balanced and well-planned diet ensures that the body has the necessary nutrients to optimize aerobic capacity and performance. It is crucial to maintain adequate carbohydrate intake to replenish glycogen stores and protein for muscle repair.
Nutritional recommendations:
- Carbohydrate: 6-10 g per kg body weight per day.
- Proteins: 127 g per kg of body weight per day.
- Fats: 20-35% of total daily calories.
- Hydration: Drink enough water before, during and after exercise.

Impact of VO2 max in different types of races.
VO2 max has a significant impact on different types of races:
Short distance races (5K, 10K): a high VO2 max allows you to maintain a faster pace during the race. At these distances, the ability to withstand high intensities for a prolonged period is critical.
Half marathons and marathons: Although VO2 max remains important, running efficiency and muscular endurance play a more important role. Runners with a high VO2 max can maintain a strong pace for longer and have a better ability to recover.
Ultramarathons: At ultra distances, energy efficiency and mental endurance are as important as VO2 max. The ability to use fat as an energy source and maintain a good nutrition and hydration strategy is vital.
Elite runners often have incredibly high VO2 maxes. For example, Norwegian long-distance runner Jakob Ingebrigtsen has reported a VO2 max of around 85 ml/kg/min, while legendary marathon runner Eliud Kipchoge has an estimated VO2 max of 84 ml/kg/min.

Training at altitude and its effect on VO2 max
Training at altitude is a strategy used by many elite runners to improve their VO2 max. The lower amount of oxygen in the air at high altitudes forces the body to adapt by producing more red blood cells and increasing oxygen carrying capacity. These adaptations can improve performance when the runner returns to lower levels, although it is crucial to carefully manage altitude training to avoid problems such as altitude sickness.
Use of technology in measuring and improving VO2 max.
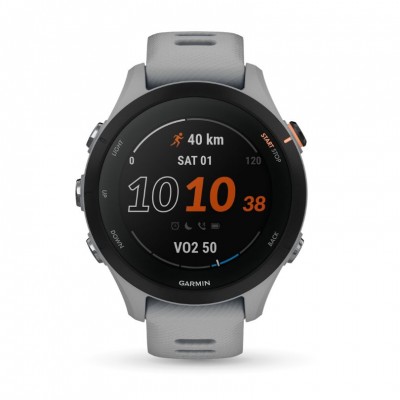
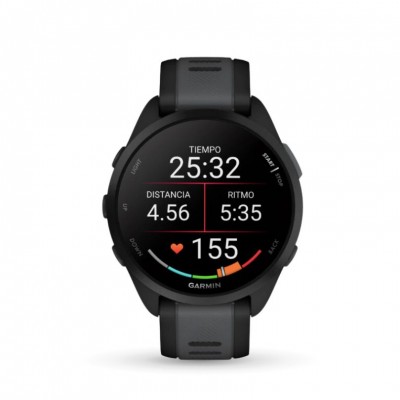
Nowadays, technology plays an important role in measuring and improving VO2 max. Devices such as advanced heart rate monitors & sports watches can estimate VO2 max based on heart rate and performance during runs. In addition, customized training applications can help design specific training programs to improve VO2 max by adjusting the training load based on the athlete's progress and recovery.

What if I am a recreational runner?
I understand that if we are popular runners, improving VO2 max may seem complicated, but with proper and consistent training, it is possible to see significant improvements. It is important to follow a personalized and balanced training program that includes both high intensity and endurance training. In addition, it is just as important to listen to your body and avoid overtraining, which can lead to injury and fatigue.
I remember when I first started training with high-intensity intervals. At first, it seemed impossible to sustain such high paces, but with time and consistency, I was able to notice a significant improvement in my performance and my VO2 max.
VO2 max is a key indicator of running performance. Understanding and improving this parameter will help us reach new levels of performance. A combination of targeted training, good nutrition and a systematic approach to improving aerobic capacity are essential to maximizing VO2 max and thus running performance. Amateur runners will also benefit from these strategies to improve our oxygen consumption capacity and thereby improve our running goals.
Read more news about: Running Training